2026.01.30
【Paper】Biosensors and Bioelectronics
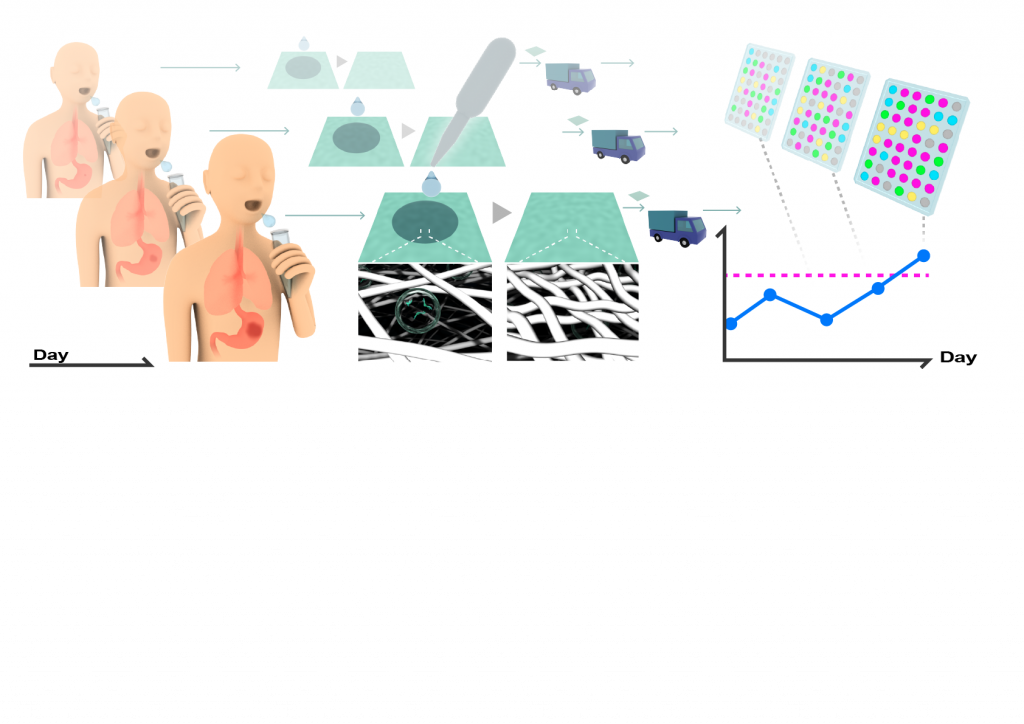
This is a research paper compiled by Assistant Professor Ajiri. By using a cellulose nanofiber sheet, the study achieves routine monitoring capable of rapidly and stably collecting and preserving exosome-derived microRNAs from as little as 10 µL of saliva, enabling the detection of variations associated with disease states and lifestyle-related factors.
Paper overview
Exosome-derived microRNAs (miRNAs) present in saliva have attracted considerable attention as promising biomarkers that reflect a wide range of disease states, including cancer and inflammatory disorders. However, conventional methods for exosome isolation and miRNA analysis, such as ultracentrifugation, require labor-intensive procedures and large sample volumes, which severely limit their applicability to routine and longitudinal monitoring.
In this study, we propose a new platform for the collection and preservation of salivary exosomes using a cellulose nanofiber (CNF) sheet, enabling routine monitoring of exosome-derived miRNAs in saliva. Owing to its high specific surface area and nanoscale porous structure, the CNF sheet can rapidly and efficiently capture exosomes by simply applying as little as 10 µL of saliva. The entire sample preparation process is completed in less than one minute and does not require any specialized equipment. Furthermore, this method demonstrates that miRNAs captured on the CNF sheet remain stable under room-temperature conditions, achieving higher miRNA recovery efficiency and superior storage performance compared with conventional approaches. Comparative studies with ultracentrifugation confirmed that the CNF sheet-based method enables highly reproducible miRNA analysis from small sample volumes.
Using salivary samples collected from healthy individuals and cancer patients, miRNA profiling successfully revealed differences in disease-associated miRNA expression patterns. In addition, continuous saliva sampling over a 20-day period demonstrated that this method can capture miRNA expression changes corresponding to lifestyle-related factors such as dietary intake, highlighting its suitability for individual-level longitudinal biomarker analysis. Taken together, these results indicate that the CNF sheet-based salivary exosome miRNA monitoring method combines non-invasiveness, rapid processing, and operational simplicity, and holds strong promise for continuous health assessment in home-based and preventive medicine, as well as for future liquid biopsy applications.
Paper information
Routine monitoring of microRNAs in salivary exosomes using a cellulose nanofiber sheet
T. Ajiri, M. Zhang, N. Mizukami, M. Iida, S. Kawaguchi, Y. Sekihara, K. Chattrairat, Z. Zhu, Y. Baba, H. Koga, and T. Yasui*
Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 299, 118436 (2026)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2026.118436
Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is a leading international journal dedicated to the research, design, development, and application of biosensors and bioelectronic devices. It is an interdisciplinary journal serving researchers interested in the use of biological materials in novel diagnostic and electronic devices.